What is the Foreign Exchange Market?
A global, worldwide decentralized financial market for trading currencies.
An over the counter market. The OTC is an electronic inter-dealer quotation system that displays “real-time” quotes, last sales prices, and volume information.
The largest and most liquid market in the world, with a daily transaction average of $6.5 trillion USD (2019)
A typical foreign exchange transaction in which a trader simultaneously buys and sells units of currency within the desired trading pair through a registered global brokerage firm.
There is profit potential regardless of market direction. (straddling the market)
Unlike other financial markets, traders can respond immediately to currency fluctuations whenever they occur day or night.
A true 24 hr. market is Sunday 5 pm to Friday 5 pm EST.
Trading begins in Sydney and moves around the globe as the business day progresses to Tokyo, London, and New York.
Who Trades Currency
in the Foreign Exchange Market?
Forex Market Hierarchy
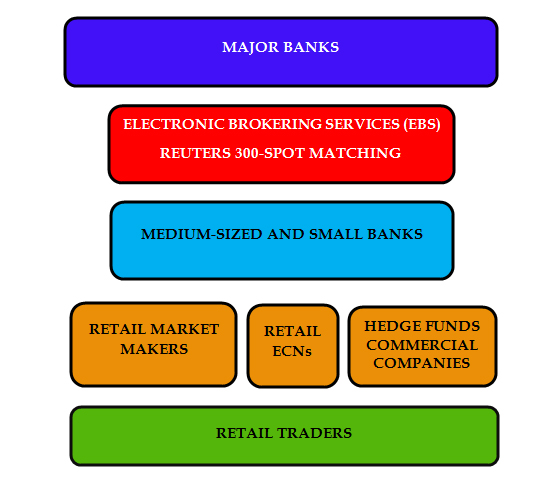
Forex Market Compared To New York Stock Exchange
There are approximately 2,800 stocks listed on the New York Stock Exchange and another 3,100 are listed on the NASDAQ. (National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations System)
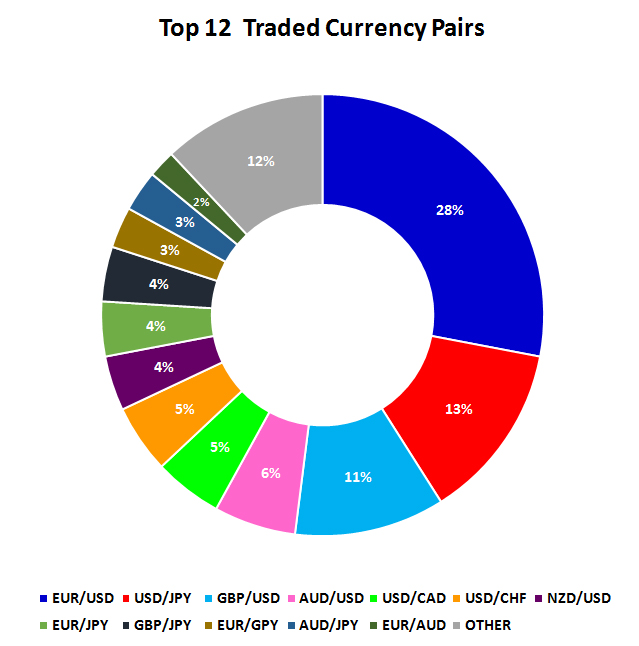
There are seven major & seven minor currency pairs that are predominantly traded in the foreign exchange market.
Volume
A sizable comparative advantage between the Forex Market and Stock Market is the sheer size of the Forex Market. The Forex Markets volume dominates the dollar volume of all the world’s Stock Markets combined together.
Liquidity
The Forex Market trades in high volume and liquidity. Liquidity leads to tighter spreads and lower transaction costs. The Forex Markets major pairs typically have extremely low spreads and transaction costs when compared to Stock Market. This is one of the major advantages of trading the Forex Market versus trading the Stock Market.
Unlike the stock/equity markets, there are no restrictions on short-selling in the currency market. Trading opportunities exist in the currency market regardless of whether a trader is long or short, independent of the market movement.
Placing Market Orders
In the Stock Market, it can take up to one day to fulfill a market order depending on the size of the order, availability of shares and the time the order is placed.
In the Forex Market, orders are instantly executed and filled under normal conditions.
Forex Market
- Volume Average $6.6 Trillion per day
- High Liquidity
- 24 Hour Markets
- Minimal or no Commissions
- Narrow Focus (8 major currencies)
New York Stock Exchange & NASDAQ
- Volume Average $450 Billion per day
- Less Liquidity
- 8 Hour Markets
- Commissions
- Wide Focus (Thousands of Stocks)
How is the Foreign Exchange Market Regulated?
Global, governmental, and independent supervisory bodies regulate the foreign exchange markets by setting standards that all brokers under their jurisdiction must comply with. These standards include being registered and licensed with the regulatory body, undergoing regular audits, communicating certain changes of service to their clients, and more.
| Country | Supervisory Bodies |
| Australia | The Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) |
| Canada | The Investment Industry Regulatory Organization of Canada (IIROC) |
| Cayman Islands | Cayman Islands Monetary Authority (CIMA) |
| Germany | Federal Financial Supervisory Authority (FFSA) |
| Hong Kong | The Securities and Future Commission (SFC) |
| Japan | The Financial Services Agency (FSA) |
| Singapore | The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) |
| Switzerland | Swiss Financial Market Supervisory Authority (FINMA) |
| United Kingdom | Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) |
| United States | The National Futures Association (NFA) |
Forex supervisory body regulators are in place is to ensure clients are protected. Regulations are strictly enforced and implemented by regulators. This protects the brokers and their clients.
By having the Forex Market regulated, it ensures the clients’ interests are protected and their investments are safeguarded. There is a regulated compensation safeguard built in place if bankruptcy occurs to a registered Forex brokerage firm.
What is a Currency Pair?
All trading within the Forex Market, whether selling, buying, or trading, will take place through currency pairs such as the EUR/USD. The first currency is known as the base (dominant) currency. The second currency is referred to as the quote or subordinate currency. The base currency acts as the basis for all transactions, regardless if it is buying or selling. A currency pair is a structure that can be bought or sold.
Top 10 Forex Daily Average Trading
Volumes (Jan 2020)
Ranking & Percentage of Daily Trades (bought or sold)
| United States Dollar | |
50.41% | 2.9 Trillion |
| European Union Euro | |
17.38% | 1 Trillion |
| Japanese Yen | |
9.62% | 554 Billion |
| British Pound | |
7.34% | 422 Billion |
| Australian Dollar | |
3.88% | 223 Billion |
| Canadian Dollar | |
2.89% | 166 Billion |
| Swiss Franc | |
2.85% | 164 Billion |
| Republic of China | |
2.47% | 142 Billion |
| Hong Kong | |
2.03% | 117 Billion |
| New Zealand | |
1.13% | 65 Billion |
Are Market Orders Placed Manually or Automated?
Both types of market orders can be placed through a registered Forex brokerage firm. Forex brokers are firms that provide traders with access to a platform that allows them to buy or sell foreign currencies in pairs.
A currency pair is the quotation of two different currencies, with the value of one currency being quoted against the other.
Before a market order is placed by a trader or automated trading system, there is a range of checks and balances to be completed, maximizing potential profit in harmony with risk management. Stop-loss and limit orders play an essential role in any market order.
A predetermined limit order allows the trader to specify the rate where the market will take profit and then exit the trade.
A predetermined stop-loss order similar to a limit order but in the opposite direction. It specifies the maximum loss that a trader is willing to accept on a given trade.
Automated trading systems have some advantages. They minimize emotional trading, allows for backtesting, preserves the trader’s discipline, and allows multiple accounts.
Experienced traders never trade out of fear, greed, revenge, or expect to make a quick profit. They have adopted a rigorous trading plan combined with well-proven trading strategies that are executed on every trade.
What is the difference between a Fundamental Analysis vs Technical Analysis?
Fundamental Analysis and Technical Analysis are paramount to any currency trader before a market order is placed. The outcome can determine if the trader should place a buy order, sell order or no market order.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental Analysis has a direct correlation with the current economic stability of any given country’s currency. Some of the key factors that determine a country’s current economic stability are interest rates, unemployment rates, inflation, retail sales, housing starts, gross domestic product, trade deficits, business inventories, industrial production, producer price index and consumer price index.
Technical Analysis
The technical analysis concentrates on historical price action, market statistics, and volume data for forecasting future market trends. Technical analysis assumes that history repeats itself. The market moves in predictable patterns, prices move in trends that are identifiable and fairly predictable.
Key factors in technical analysis are technical indicators, technical theories, and the technical analysis of chart patterns.
